- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Requirements
- Citrix scanning requirements
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
08-27-2018
08:30 PM
- edited on
08-04-2023
06:51 PM
by
sophie
![]()
Ideally, a Citrix XenServer host is scanned through the Citrix API (XenAPI or XAPI). Though other protocols enabled on the XenServer, like SSH, may provide some information as well, the XenAPI will return the most detailed data.
In order for Lansweeper to scan a XenServer host, you need to ensure that TCP port 443 is opened on the XenServer host and that the HTTPS title contains the text "XenServer" or "Citrix Hypervisor".
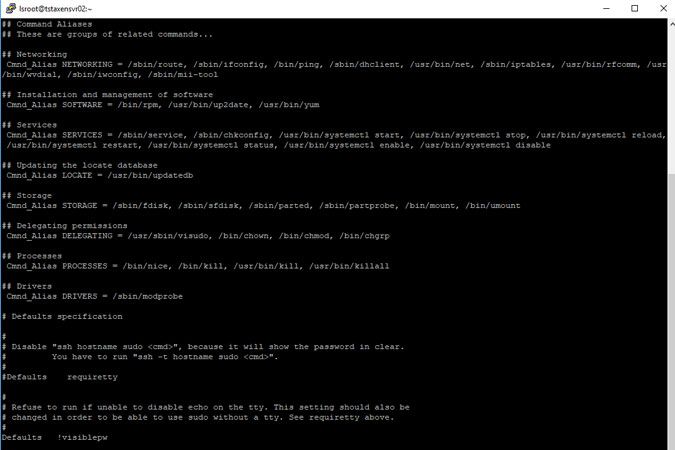
The account you use to access the XenAPI must be able to run following command aliases NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS.
Full root access is not necessary.
The HTTPS title of the machine must contain the text "XenServer" or "Citrix Hypervisor" in order for the machine to be correctly identified as a XenServer. Custom HTTPS titles are not supported at this time.
Use our devicetester to check if TCP port 443 is open on the XenServer and to check that the HTTPS title is correct.
To configure a XenServer host for scanning, follow these steps:
- Logon as root to the XenServer console via an SSH session.
- Create a user to scan your XenServer host. You can use the standard Linux useradd command. In below example we created a user called lsscan.
useradd -c "LansweeperScanCred" -d /home/lsscan -s /bin/bash lsscanA short explanation of the used parameters:
-c: Any text string. It is generally a short description of the login.
-d: The new user will be created using this value as the user's login directory.
-s: The name of the user's login shell. - Set the password for the newly created user.
passwd lsscan - Open the sudo config file to grant the newly created user the required permissions.
visudo - Edit the sudo config file and uncomment (removing the # before) the following command aliases: NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS
- Assign the command aliases to the newly created user by adding the following line at the bottom of your sudo config file:
lsscan ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS - The newly created user and password can now be used to scan the Citrix XenServer.
More information on how to enter your newly created Citrix credentials can be found in this knowledge base article.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try NowNew to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now